Limestone Calculator to estimate base volume, weight, cost & trucks. Includes compaction allowance, 20mm vs 40mm size guide, and compacted thickness specs.
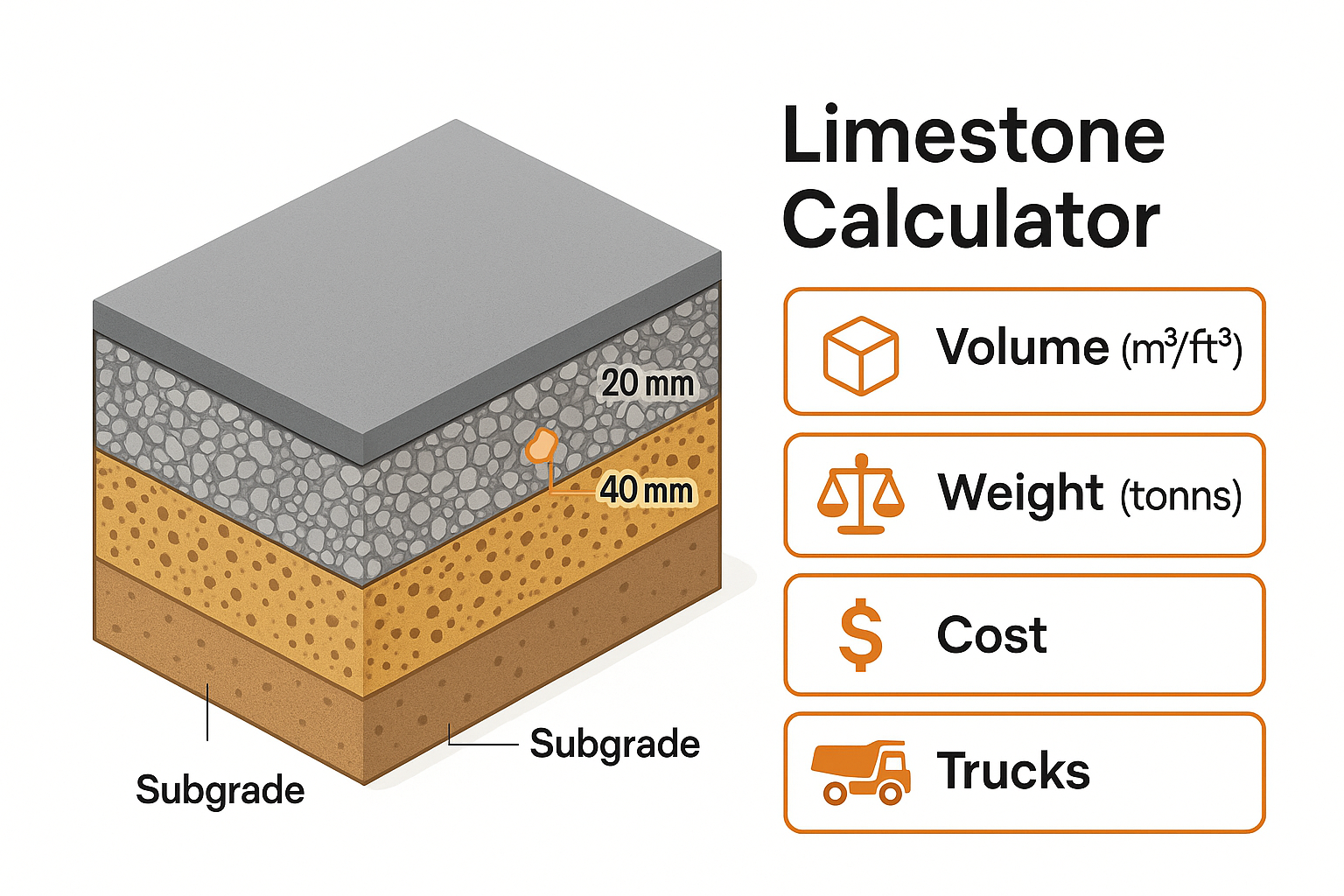

Limestone Calculator to estimate base volume, weight, cost & trucks. Includes compaction allowance, 20mm vs 40mm size guide, and compacted thickness specs.