Septic Tank Calculator to estimate ideal size, components, and cost for any project. Includes standards presets, SI/Imperial, and market-based pricing.
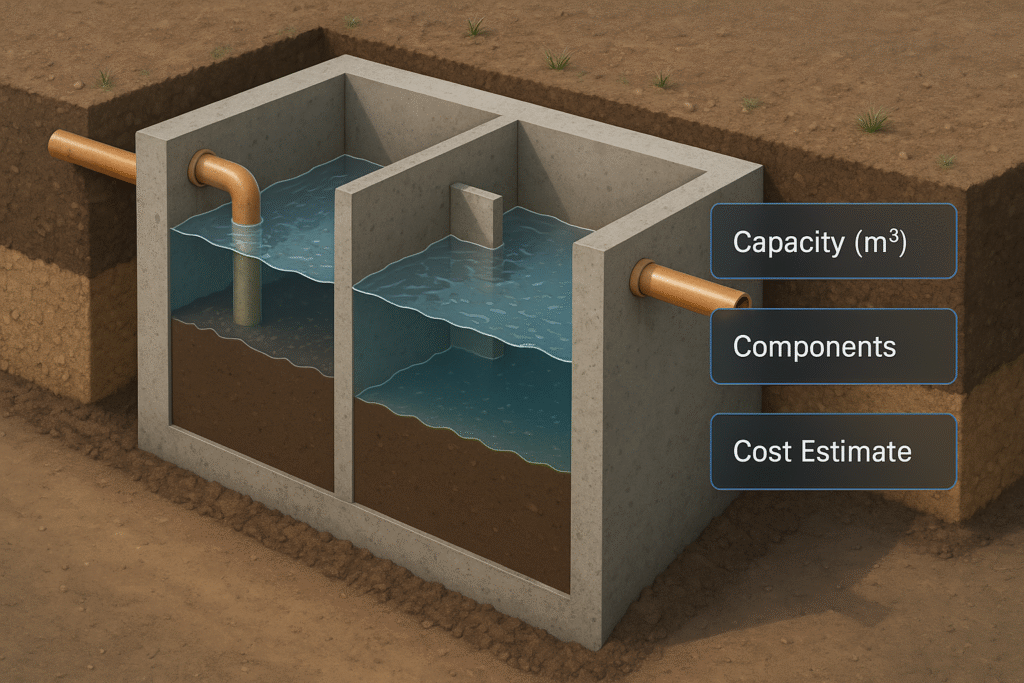

Septic Tank Calculator to estimate ideal size, components, and cost for any project. Includes standards presets, SI/Imperial, and market-based pricing.